Tretinoin vs Retinol. Which retinoid to use to prevent skin aging? Which one is safer? These are the common questions on your mind when selecting a skincare product to prevent aging skin.
Tretinoin and retinol are both skincare ingredients that belong to a class of compounds known as retinoids. They are widely used to treat various skin concerns, primarily related to aging and acne. However, they differ in terms of potency, mechanism of action, and availability.
Basically, retinoids are both natural and synthetic derivatives of vitamin A which are used to replace vitamin A. This is because vitamin A, at higher doses, is toxic (1).
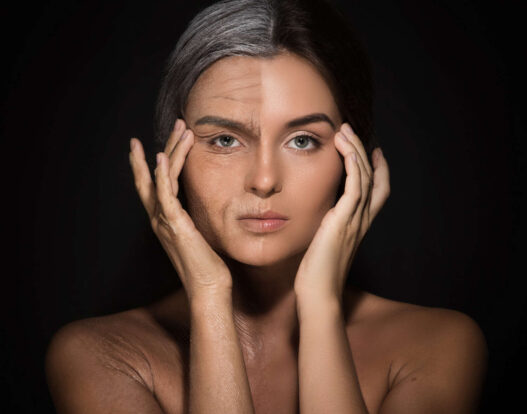
Both tretinoin and retinol are widely used to prevent skin aging. Before we delve into tretinoin vs retinol differences, let us first understand why skin aging occurs.
Skin Aging
Skin aging is a natural and gradual process as we age. It is a result of the combined effects of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. There are two types of aging – extrinsic and intrinsic aging.
Intrinsic or Natural Aging
This is a progressive degeneration of the skin that occurs with age and causes the skin to be pale, thin, fragile, dry, and finely wrinkled.
Extrinsic Aging
This is a result of exposure to a variety of factors. Ultraviolet light, infrared and visible light, pollution, cigarette smoking, and factors like nutrition, sleep, and stress, all play a role in skin aging. While all the factors contribute, UV light and oxidative stress have the most profound effect.
Photoaged skin is characterized by deep coarse wrinkles and hyperpigmentation.
Whenever there is oxidative stress, there is a breakdown of collagen by metalloproteinases (MMPs) resulting in impaired dermis functioning and exaggerated skin wrinkling. The increased skin aging has resulted in several over-the-counter products being used these days.
Tretinoin and Retinol are both derived from vitamin A, useful in skin aging as topical creams to reduce wrinkles and fine lines. So, which one to use? Let us understand how they are different. Let us compare tretinoin vs retinol.
What is Tretinoin?
Tretinoin (also known as retinoic acid) is a retinoid, and a derivative of vitamin A. It is considered more potent than retinol. Topical tretinoin has been approved for use in dermatology for over 40 years. It is a prescription-strength retinoid.
Among the retinoids, tretinoin is considered the most effective agent with proven antiaging effects on the skin. Tretinoin is currently approved for the treatment of acne vulgaris and photodamage (2), however, it is also used for facial wrinkles and hyperpigmentation (3). Thus, the uses of topical tretinoin approved by the FDA are:
- Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
- Adjunctive treatment for Photoaging:
- Fine facial wrinkles
- Skin roughness
- Facial hyperpigmentation (4)
Tretinoin, as a very thin layer, is applied once daily, before bedtime, to the skin where lesions are present. One has to keep the medication away from the eyes, mouth, nasal creases, and mucous membranes. Topical tretinoin is usually available in 0.1%, 0.08%, and 0.04% concentrations (4).
How Does Tretinoin Work?
Tretinoin works by binding to retinoic acid receptors in the skin cells, which helps to regulate cell turnover, stimulate collagen production, which is the primary building block of your skin, and increase skin cell differentiation. This leads to improved skin texture, and reduced appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and hence acts as an antiaging treatment. Further, it can also help with acne by preventing clogged pores.
Tretinoin Side Effects
Due to its potency, tretinoin may cause more significant initial irritation and peeling, and it’s typically recommended for use under the supervision of a dermatologist.
The adverse effects of topically administered tretinoin include pruritus, skin pain, skin/subcutaneous irritation, erythema, and pharyngitis.
Below we will compare the side effects of tretinoin vs retinol.
Topical tretinoin contraindications i.e., when not to use tretinoin
- Hypersensitivity to the drug, drug class, or drug formulation components
- One has to exercise caution if hypersensitivity to fish products (0.05% gel, 0.05% lotion forms). This is because some tretinoin preparations contain fish protein or fish collagen.
- Caution must be exercised when tretinoin is used in persons with sunburn, photosensitivity, or eczema.
- It is not recommended in 1st trimester of pregnancy.
Monitoring for Topical Tretinoin Use
- When used topically, monitoring for hypersensitivity, photosensitivity, and any other skin irritation or allergies is recommended.
- Symptoms of overdose with topical tretinoin use may include excessive redness, peeling, and discomfort (4).
Benefits of Tretinoin for the Skin
Treats Acne
Tretinoin for acne is a popular treatment due to its ability to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and prevent the formation of new acne lesions. It can be used to treat both comedonal acne (blackheads and whiteheads) and inflammatory acne (papules and pustules).
Fades Hyperpigmentation
This strong retinoid can improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation, including sunspots, age spots, and post-inflammatory pigmentation caused by acne. It works by increasing cell turnover and exfoliating the outer layer of the skin, revealing fresher, brighter skin underneath.
Prevents Photodamage
By increasing the skin’s natural defense and repairing existing damage, tretinoin can help prevent photodamage (damage caused by exposure to the sun’s UV rays).
Studies show that tretinoin reverses photoaging or sun damage, smoothes out fine lines and wrinkles, increases collagen, and makes the skin look firmer.
What is Retinol?
We have understood tretinoin. Now let us understand Tretinoin vs Retinol and which retinoid wins. Retinol, as compared to tretinoin, is a milder over-the-counter (OTC) retinoid. It is also derived from vitamin A, but retinol needs to undergo conversion within the skin into its active form (retinoic acid) before it can exert its effects. Because of this conversion process, retinol is generally less potent than tretinoin.
Retinol, like tretinoin, improves fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. It also improves the appearance of photoaged skin by reducing skin roughness. In addition, it offers many of the same benefits as tretinoin, such as promoting collagen production and improving skin texture, but its effects might be seen more gradually and with less risk of severe irritation compared to tretinoin.
The efficacy and tolerability of retinol make it preferable to prescription retinoids such as tretinoin (5).
However, as retinol is not FDA-regulated, the amount of retinol in formulas may be different.
Benefits of Retinol for the Skin
Reduces fine lines and wrinkles
Retinol has been shown to increase collagen production in the skin, which can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Improves skin texture
Retinol can help improve skin texture.
Treats acne
By increasing cell turnover and exfoliating dead skin cells, retinol can help treat acne by unclogging powers and reducing inflammation.
Reduces hyperpigmentation
This retinoid can help reduce the appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tones by increasing cell turnover and exfoliating dead skin cells.
Who should try Retinol?
- For most people, retinol is going to be the best first choice for retinoid treatments.
- If you’re just starting a new regimen, you can apply retinol cream every other day at first, so your skin has more time to adjust to the treatment.
- If you’re not seeing the desired effects after 2 to 3 months, you can always try switching to a higher percentage retinol cream. These are OTC medications, so you can switch to a lower or higher concentration as you see fit.
- Be on the lookout for adverse reactions whenever you change your retinol treatment.
- If you’ve tried retinol and haven’t gotten the results, you’re after, you might think about switching to tretinoin.
Tretinoin vs Retinol Side Effects
Tretinoin being stronger than retinol has more side effects. Tretinoin can cause skin redness, dryness, peeling, and sun sensitivity.
Retinol has fewer side effects. There may be redness and some dryness, but no peeling.
Despite being widely used for many years, like most skincare products, both tretinoin and retinol have potential side effects. Although they share similar side effects, tretinoin has been known to have a greater risk of side effects than retinol – due to its strength.
Some of the potential side effects are:
Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
This means dark patches form on areas of the skin. If we compare tretinoin vs retinol, although both can treat hyperpigmentation, they can also cause it if you use too high a concentration or frequency initially.
Photosensitivity
Using retinol may increase skin sensitivity that can significantly enhance your chance of sunburn and sensitivity to other skincare products. To avoid this, you will need to use sunscreen daily. Here is our sunscreen guide to select the best one.
Irritation
Retinoid creams have a high concentration so they can cause irritation of the skin.
Teratogenicity
There are some pregnancy risks associated with Vitamin A which may affect foetal development.
Tretinoin vs Retinol – In Summary
Tretinoin
- Prescription-strength.
- Directly binds to retinoic acid receptors.
- More potent and effective.
- More likely to cause irritation, redness, and peeling, especially initially.
- Often used for more severe acne and pronounced signs of aging.
- Requires a doctor’s prescription.
Retinol
- Available over the counter.
- Needs to be converted into retinoic acid by the skin.
- Generally milder and better tolerated, especially for sensitive skin.
- Effects may be seen more gradually than with tretinoin.
- Commonly used for mild to moderate signs of aging and general skin improvement.
Tretinoin vs Retinol – What’s the difference?
- Retinol is naturally derived from vitamin A, while tretinoin is synthetic.
- Tretinoin is significantly potent (about 20 times more potent) and stronger than retinol. However, the products are not the same. It is considered stronger because tretinoin or retinoic acid is a form of vitamin A that works directly on the skin to boost cell renewal, turnover, and DNA damage repair.
- With a higher potency than retinol, tretinoin is more effective in acne treatment and will achieve faster results when treating signs of skin aging.
- Retinol takes a longer time to show any visible effects on the skin. This is because when retinol is applied to the skin, enzymes are required to convert it into retinoic acid.
- Tretinoin is only available with a prescription from a dermatologist or other appropriately licensed medical professional, while retinol compounds are typically over the counter.
- Typical skin shedding and other side effects during early use of retinol are less pronounced than tretinoin. Because retinol has a lower concentration, the irritation it causes will likely be less severe.
- Tretinoin, but not Retinol, is regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The choice between tretinoin and retinol depends on your specific skincare goals, skin type, and tolerance for potential irritation. The clinical use of tretinoin has been limited due to possible skin irritation or retinoid dermatitis (6). For the latter, retinol has an edge over tretinoin. But tretinoin may be more potent and efficacious.
If you’re considering incorporating either of these into your skincare routine, it’s a good idea to consult with a dermatologist to determine which option is best suited for your needs.Top of Form
Tretinoin vs Retinol – The Final Verdict
Retinol and tretinoin are two forms of vitamin A that have different properties and effects on the skin. While they both have benefits for reducing fine lines and wrinkles, improving skin texture, treating acne, and reducing hyperpigmentation, tretinoin is more potent, and effective and can cause more side effects than retinol. It is important to consult with your dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31643883/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23839179/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36220974/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557478/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35816071/
- https://jddonline.com/articles/supplement-article-retinol-the-ideal-retinoid-for-cosmetic-solutions-S1545961622S00s4X/.