Over the years, we’ve seen several interesting innovations in orthopedic and musculoskeletal medicine. The advent of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments was a massive step in the right direction for many. Then came stem cell therapy, which has also become increasingly popular. All of these developments are part of a broader movement called Orthobiologics. The term ‘Orthobiologics’ has now been used more extensively in some circles, although not everyone understands what it means.
To clear out the confusion, we’ll break this term down and explain why you should care about Orthobiologics.
Orthobiologics – What Are they?
As I said, the term “orthobiologics” has become very popular recently. And like every popular trend, there’s always a tendency for people to use it wrongly.
To better understand Orthobiologics, let’s break the word into its main components – “ortho” and “biologics.”
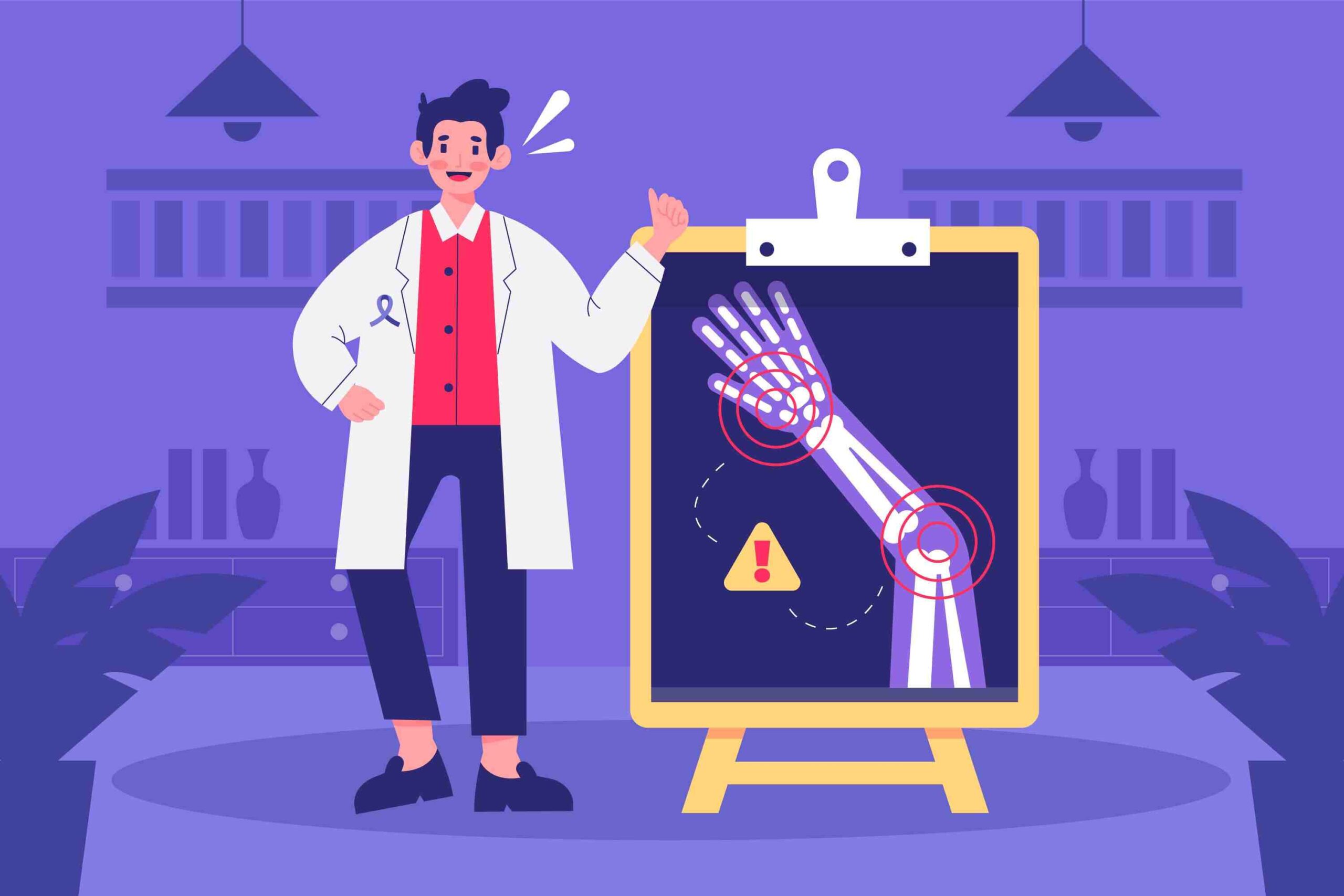
“Ortho” is a popular medical term that references straightening or repairing. It is usually applied when it comes to bones, ligaments, tendons, joints, and muscles. On the flip side, “biologics” are substances that can be naturally derived from the body. So, combining these two terms essentially alludes to substances in the body that help to heal your joints, bones, muscles, and so on.
When it comes to healing your body, Orthobiologics play a major part. This is especially true for people dealing with injuries and other conditions that affect the regular functioning of their muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments, etc.
Categories of Orthobiologics
Generally, orthobiologics can be categorized based on two primary factors:
- Their sources
- The types of tissues being used
Orthobiologics – Sources
As explained, orthobiologics are substances derived from the human body. So, these substances can either be acquired from your body or someone else’s. When examining sources, we can further classify orthobiologics into two – autologous and allogeneic.
Autologous orthobiologics
Autologous orthobiologics are those substances that are obtained from the person it’s been used on. So, when a doctor draws blood from your veins to extract platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and injects these same PRPs into a damaged tendon in your body, those PRPs are autologous Orthobiologics.
Allogeneic orthobiologics
If the substance is received from someone else’s body, it’s an allogenic orthobiologics. Birth tissues from someone else that is applied to another person’s body are Allogeneic Orthobiologics.
Orthobiologics – Tissue Types
This is where we have a more broad classification. There are generally four types of Orthobiologic substances. They include:
Blood-Derived Orthobiologics
The name pretty much says it all, doesn’t it? Blood-derived Orthobiologics are substances obtained from the blood – whether that of a patient or someone else.
A perfect example of blood-derived Orthobiologics would be platelet-rich plasma. A doctor takes blood from a patient, processes it to get the PRP by removing the red and white blood cells, then re-injects the portion with high platelet into the area that requires healing.
PRP is beneficial because platelets help to speed up healing. PRP can be a very important form of support when it comes to healing your body. It can be very advantageous when injected into an area of tissue or muscle damage. Different types of PRP can depend on the concentration of cells and how they are processed or activated.
There is also platelet-poor plasma (PPP). These are PRPs with a much lower concentration of platelets. While PPPs don’t contain much of the critical platelet component, they also contain different cytokines and plasma-based growth factors that can help in healing. PPP has been shown to aid muscle healing and reduce the breakdown of cartilage.
Stem Cells
Stem cells come in different parts – including autologous, allogenic, and culture-expanded.
Autologous stem cells, which are acquired from the body, tend to be derived mostly from excess fat and bone marrow. Through bone marrow aspirate procedures, a needle is inserted into the hip bone and the bone marrow is carefully extracted. Then, the bone marrow is processed and the stem cells or also called medicinal signal cells (MSC) are collected.
As explained, allogenic stem cells are those stem cells from the body of another person. Other examples such as Wharton’s jelly and amniotic fluid are allogenic, it has been purported to be stem cells but recent studies do not suggest that. There has been some research to dispute their concentration of stem cells, although they’ve been marketed otherwise. For now, these products are quite controversial.
Then, there are culture-expanded stem cells. These are perhaps the most controversial of them all. The process of obtaining these cells includes isolating and growing a massive number of stem cells from birth tissue, fat, or bone marrow. For now, cultured expanded stem cells are not approved for use in the United States.
Extra Cellular Matrix
Also known as ECMs, these are orthobiologics that offer important support to your body’s cells. They act as fillers, stepping into large gaps in torn tissue. This way, they operate as a bridge that enables the formation of new cells in the damaged area.
As cells conduct repairs, they need something to aid their growth. ECM orthobiologics help in this regard, working like scaffolding. At the same time, many of these Orthobiologics also contain growth factors and chemicals that make your body’s cells work harder. Thus, they could speed up the healing process exponentially.
Some popular examples of ECM orthobiologics include birth tissues from fat grafts (also known as Lipoaspirate), and demineralized bone matrix (DBM).
Conditioned Media
The final class of orthobiologics is conditioned media. These are products and substances being described as “exosomes,” and they are usually tiny information packets that are from living cells.
Exosomes primarily are small bubbles that are obtained from cells. They are incredibly small, and they contain important information from cells that influence how other cells work. Essentially, these exosomes are how cells communicate.
We can find exosomes in most bodily fluids – including urine, blood, saliva, and even breast milk. They are released rapidly and in large quantities. However, research is still ongoing into their effects, and even the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) has warned about their use for now.
Orthobiologics – What’s In It for You?
Right now, many believe that orthobiologics is the next phase of evolution for orthopedic medicine. We’ve seen cases of stem cell therapy being used to treat ACL tears for professional athletes and in other conditions such as knee and hip osteoarthritis. PRP has also been applied in tears on the rotator cuff, tennis elbow, knee osteoarthritis and gluteus tendon tear.
With orthobiologics, the hope is that patients can avoid or delay surgical procedures and instead use less invasive and complex treatment processes to take care of issues in their bones, ligaments, muscles, joints, and more.
As orthobiologics get more advanced, there is a high likelihood that we might be slowly starting to avoid some invasive surgeries. Orthobiologics have the potential to help with healing your body while reducing the complications, risks, and healing timeline of traditional surgery.
Orthobiologics: The Need for Caution
Reading all of this, it’s easy for you to believe that orthobiologics will essentially cure everything we’ve been dealing with as humans. And, it’s true – Orthobiologics is a very interesting field that is gaining more attention from everyone. It has shown promise when it comes to treating several severe injuries and cases of joint, muscle, ligament, and tendon damage, amongst others.
The prospect of offering non-invasive surgery is also very attractive, and it is one of the reasons why many are interested in orthobiologics. In theory, it could reduce the time taken to recover from several injuries and improve the efficacy of treatment.
However, this innovation isn’t without its controversies. Many have pointed out that orthobiologics might not be as transformative as they claim to be, and they have proof of a lot of people who have received some “Orthobiologics procedure” or the other and who haven’t quite benefited from it.
Stem cell therapy has received some criticism. Over the past few years, we’ve seen an increase in the number of fake stem cell therapy treatments that promise the world, only to be revealed as complete shams.
However, this doesn’t mean that orthobiologics is ineffective. There are compromised medical therapy practitioners who offer untested therapies just for the purpose of making a quick buck. But, these people shouldn’t be allowed to abuse the name of this up-and-coming medical innovation.
It is also worth noting that orthobiologics are still evolving. There’s a lot about the procedures that are still being found out, and additional clarity will be required for this field to really live up to its potential. As more research efforts and tests are being carried out, medical professionals will be able to understand how best to apply Orthobiologics for the benefit of mankind and truly save lives.
This is why it is more important than ever to only get orthobiologics and other related therapies from accredited and licensed practitioners. Right now, these are the only people who have the skills and expertise to help you. They also understand the level of advancement that orthobiologics have and will be able to offer the right counsel.
If a licensed medical professional offers to perform an orthobiologics procedure, you’re more confident that they will work within the limits of their expertise and legally-permitted parameters. Right now, working with them is the best way to guarantee a safe procedure.

Dr. Oluseun Olufade, MD, is an Assistant Professor of Orthopedics at Emory School of Medicine. He is board-certified in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Sports medicine, and Interventional spine. Dr. Olufade practices sports medicine and spine care with a special interest in youth sports, active adult, regenerative medicine/Orthobiologics, and soccer medicine. He treats adolescents and adults, and his patients range from middle school students to professional athletes. Dr. Olufade is currently a physician for several athletic teams and organizations, including U.S. Soccer Physician Network, Atlanta Hawks, Emory University, Northview High School, and Mt Pisgah Christian School. He is also actively involved in the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine (AMSSM), where he serves as Co-Chair of Ultrasound Instructional Course Lecture, and Chair for the Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R) curriculum subcommittee.